The Set Up
Following my own advice, I perform a year-end Annual Product Performance Review (APPR) which revealed some startling results. Even after 30 years of  managing medical device product lines my APPR revealed that I was spending a disproportionate amount of time working on non-business imperatives. To optimize your contribution to the company imperatives you need to periodically ask yourself, “How am I doing?”
managing medical device product lines my APPR revealed that I was spending a disproportionate amount of time working on non-business imperatives. To optimize your contribution to the company imperatives you need to periodically ask yourself, “How am I doing?”
It is easy to take advantage of opportunities and correct issues once you discover them, but if you never look, oh well.
So as obvious as the need for APPRs are, a number of my fellow marketers aren’t doing them. Why? They would go ballistic is their supervisors failed to do an annual performance appraisal on their own performance.
If you are a serious Product Manager you will have already set up monthly metrics to keep track of your new products (those less than 1 year old). Have you looked at your entire portfolio? No? I am willing to wager that if you do you will discover some amazing things that if acted upon will increase your portfolio performance in 2017.
Annual Product Performance Reviews
I call this maintenance activity an APPR. As a product manager we have to care for our product lines, particularly when they have been on the market for a while and the excitement of the launch has worn off. Spending one day a year, on each of your product lines is a minimal amount of your time invested that could prevent you from being shaken from a good night sleep by an overlooked issue. What kind of an issue? Quality shifts, pricing slip, share slip, new competitive entry, shifting sales force focus, slipping gross margins, resurgence, increasing complaint levels all these potential issues are leading indicators of critical times for your product line.
The APPR can be done anytime of year. At its core, is a year-over-year comparison of key metrics. The more years you have data for, the more likely you are to see a trend. It is good to partner with finance or IT the first time you conduct this type of analysis to make sure your data sources are complete and comparable. For some product lines a monthly review may be more appropriate.
Each APPR took a day and included a review of the following metrics
- Units, total
- Unit, mix
- Average selling price (ASP)
- ASP by mix
- Complaint rate by type or category
- Manufacturing yields
- Gross margins (GM)
- Revenue
- Revenue distribution my geography
- Revenue distribution by sales territory
- Number of active accounts
- Number of accounts that went inactive over the past 12 months
- NEW! As accurately as you can estimate the amount of time you are spending on the various products in you portfolio.
These metrics are all loaded into a simple excel file, which automatically did the year-over-year trend comparison and some simple charting. The output was the APPR dashboard. Often this dashboard pointed towards areas that needed my attention and a bit of investigative work.
Today, I have created custom dashboards in salesforce.com that provides real time comparisons for new product launches, after one-year the dashboard changes to a periodic based trend analysis that has taken the place of the APPR dashboard. The important thing is to monitor the product lines you are responsible for and take nothing for granted. This is a good application of the, “productive paranoia” concept that Jim Collins discusses in his book, Great by Choice.
Career Building Opportunity
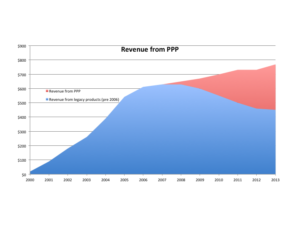
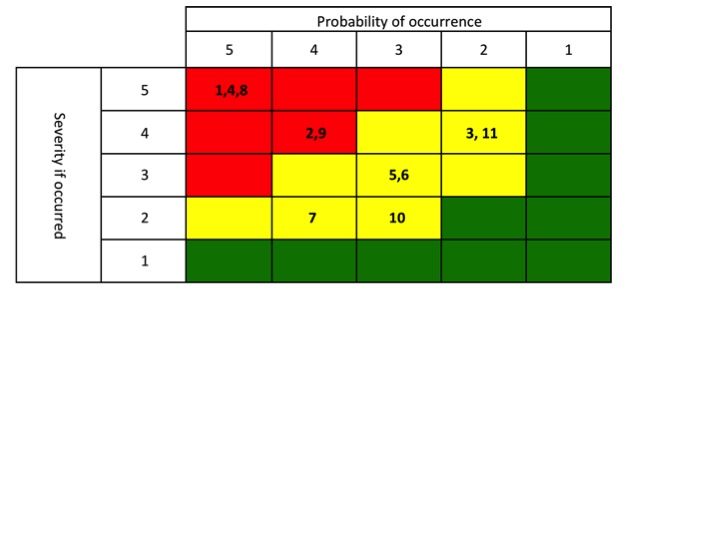
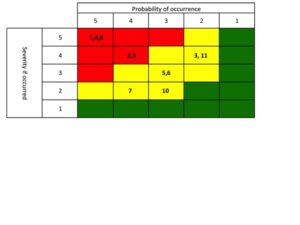
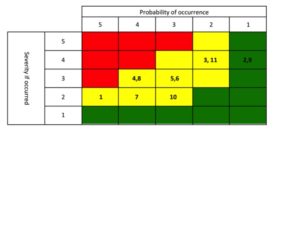
Once you have performed the review, packaging a “winners and losers” list is a great way to communicate to Sr. Management about the performance of their products (keep it simple – see example to the right). Everyone who doesn’t pay as close attention to your portfolio as you do would view this as a valuable tool. Now the challenge is that you are then compelled to act on the findings. Plan out 1-3 communications prior to publishing the list.
great way to communicate to Sr. Management about the performance of their products (keep it simple – see example to the right). Everyone who doesn’t pay as close attention to your portfolio as you do would view this as a valuable tool. Now the challenge is that you are then compelled to act on the findings. Plan out 1-3 communications prior to publishing the list.
- Information
- Reflection
- Recommended action
Make sure your supervisor knows what you are doing and why.
If any one in your organization thinks that publishing a well-done Annual Product Performance Review is a bad thing; take a look at that and ask are the reasons political, personal, or other. You can’t change what you don’t measure.
“Experience is what you get, right after you need it most.”
Make it a great day,
Tim Walker
Tim Walker is the Principal consultant for The Experia Group. A small consulting firm that specializes in providing experience and expertise during critical device commercialization phases to increase the probability of success. www.theexperiagroup.com. Contact The Experia Group for a free 30-minute consultation to determine if 30-years of experience can contribute to your success.
© 2017, The Experia Group, LLC